Your Ring doorbell suddenly stops sending motion alerts or the live view freezes when you try to check who’s at the door. Before calling customer support or assuming your device is broken, the culprit is likely your Wi-Fi connection. This happens to thousands of homeowners daily—especially after router updates or power outages. Checking your Ring doorbell’s Wi-Fi status is the fastest way to restore security features without unnecessary stress.
This guide delivers precise, step-by-step methods to verify your Ring’s Wi-Fi connection, diagnose specific network issues, and implement solutions that actually work. You’ll discover both quick app-based checks and advanced troubleshooting techniques that most Ring users never try—saving you hours of frustration and potential service calls.
Check Your Ring App Device Health Status
Access Real-Time Wi-Fi Connection Data
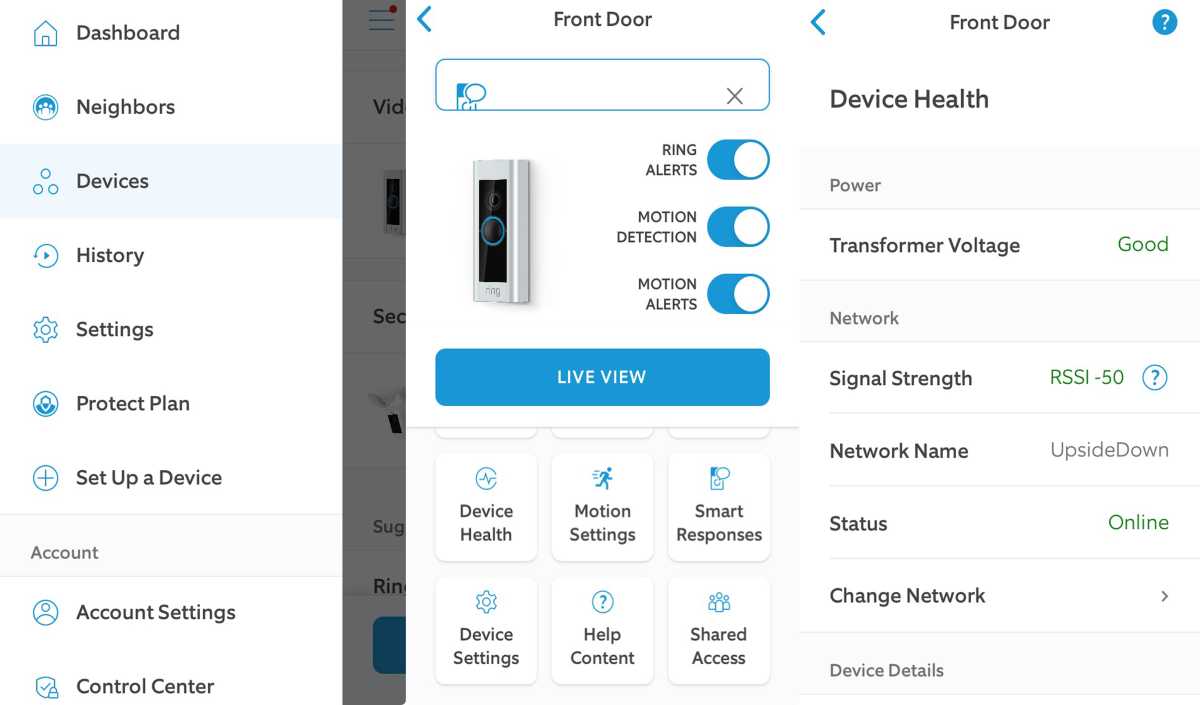
Open the Ring app and tap the three-line menu icon in the top-left corner. Select Devices, then choose your specific doorbell model. Navigate to Device Health where you’ll see your current Wi-Fi connection status, network name, signal strength indicator, and last connection timestamp. This screen provides immediate insight into whether your doorbell maintains proper network communication.
Interpret Signal Strength Indicators Correctly
Your Device Health page displays Wi-Fi signal as Good, Fair, or Poor. Good means stable connectivity for all features including HD video streaming. Fair indicates marginal signal that may cause intermittent notification delays or frozen live views. Poor means your doorbell struggles to maintain any connection—expect frequent disconnections. If you see “Offline” with no signal reading, proceed to network diagnostics immediately.
Verify Your Home Network Functionality First
Test Wi-Fi with Another Device on Same Network
Before blaming your Ring doorbell, confirm your home network works properly. Connect your smartphone or laptop to the exact same Wi-Fi network your Ring uses. Stream a video or load multiple web pages for 30 seconds. If this secondary device connects without issues, you’ve eliminated internet outages as the root cause—focusing your troubleshooting on Ring-specific factors.
Assess Router-to-Doorbell Distance and Obstructions
Stand at your doorbell’s mounting location and count how many walls separate it from your router. Each wall—especially those with metal studs or concrete—significantly degrades signal strength. If your doorbell sits more than 30 feet from the router with multiple barriers, signal degradation likely causes connectivity problems. Pro Tip: Temporarily move your router closer to test if distance is the issue before investing in extenders.
Fix Wi-Fi Password Authentication Failures
Validate Password Accuracy and Format
Incorrect passwords prevent Ring doorbells from connecting entirely. Double-check you’re entering the correct credentials—check the label on your router’s bottom if using default settings. Crucially, ensure your Wi-Fi password contains no asterisks (*) or pound signs (#), as these characters cause authentication failures with Ring devices. Access your router’s admin page to modify the password if problematic characters exist.
Avoid Common Password Mistakes During Setup
When reconnecting your Ring doorbell, watch for these frequent errors: mixing up similar characters (0 vs O, 1 vs I), entering password in wrong field, or using guest network credentials instead of main network. Write your password on paper first, then carefully input it during setup. If your network uses special security protocols like WPA3, temporarily switch to WPA2 for compatibility during Ring setup.
Confirm 2.4 GHz Network Compatibility

Determine Your Ring Model’s Band Support
Not all Ring doorbells support 5 GHz networks. Check your specific model’s specifications—older models like Ring Video Doorbell 2 only work on 2.4 GHz. If your router broadcasts both bands under the same network name (SSID), your doorbell may attempt 5 GHz connection and fail. Critical: Connect to a dedicated 2.4 GHz network first, as this band offers better range and wall penetration ideal for outdoor devices.
Switch Between Wi-Fi Bands Successfully
After establishing initial connection on 2.4 GHz, you can attempt migration to 5 GHz for faster speeds if your model supports it. Open Ring app → Device Health → Change Wi-Fi Network and select your 5 GHz network. Monitor performance—if live view loads faster without disconnections, keep 5 GHz. If problems return, revert to 2.4 GHz for reliability. Most users achieve best results with 2.4 GHz due to superior range.
Diagnose Battery Power Impact on Wireless Models
Check Battery Level Before Wi-Fi Troubleshooting
Low battery directly affects Wi-Fi connectivity in wireless Ring models. In the Ring app, navigate to Device Health and verify your battery percentage. Below 20%, your doorbell may disconnect intermittently or refuse to connect to Wi-Fi entirely. Warning: Troubleshooting Wi-Fi while battery is low yields false results—always check power status first.
Charge Properly Before Network Testing
If battery is depleted, charge your Ring doorbell for 6-8 hours until full. A partially charged battery won’t maintain stable Wi-Fi connections during diagnostics. During charging, keep the device near your router to prevent disconnection during setup. After full charge, wait 10 minutes before attempting Wi-Fi reconnection—this allows internal systems to stabilize.
Eliminate Physical Signal Obstructions
Identify and Remove Signal-Blocking Objects
Walk the path between your router and doorbell location. Remove or reposition furniture, metal shelves, appliances, or electronic devices blocking this path. Even moving your router 2-3 feet away from a metal desk can dramatically improve signal strength to outdoor locations. Pay special attention to microwave ovens, cordless phones, and baby monitors which operate on similar frequencies and cause interference.
Implement Strategic Signal Boosting Solutions
When router relocation isn’t feasible, install a Wi-Fi extender specifically designed for Ring devices. The Ring Chime Pro serves dual purposes as both a Wi-Fi extender and internal doorbell chime. Position it halfway between your router and doorbell for optimal signal boost—typically 15-20 feet from each. Avoid placing extenders near large metal objects or water sources which degrade signal quality.
Execute Network Reset Sequence Properly

Perform Correct Router and Modem Restart
Power cycle your network equipment using this precise sequence: unplug both modem and router, wait exactly 30 seconds (critical for clearing memory), plug modem back in first and wait 2 minutes for full initialization, then plug router in and wait 2 minutes. Test internet connectivity with your phone before checking Ring—this clears temporary network glitches affecting Ring connectivity.
Reconnect Ring to Wi-Fi After Network Reset
After network restart, reconnect your doorbell using the Ring app: select your doorbell → Device Health → Reconnect to Wi-Fi. Carefully enter your network name and password—watch for case sensitivity. Wait 2-3 minutes for connection establishment; the status light on your doorbell will turn solid blue when successful. If it flashes white or blue repeatedly, check password accuracy and try again.
Perform Factory Reset as Last Resort
Prepare for Reset Procedure Safely
Before factory resetting your Ring doorbell, download and save any important videos from the Ring app—this process erases stored footage. Ensure you have your Wi-Fi password and account credentials ready, as you’ll need to complete full device setup again. Locate your specific model’s reset button (usually orange and recessed) and a paperclip for access.
Execute Reset and Reconfigure Correctly
Press and hold the reset button for exactly 20 seconds using a paperclip, then release. The status light will flash rapidly indicating reset initiation. Wait 30 seconds for completion, then open the Ring app and select “Set Up a New Device.” Follow prompts to reconnect to Wi-Fi—this resolves deep software issues preventing network connection. Note: Hardwired models may require temporary power disconnection during reset.
Prevent Future Wi-Fi Disconnections Proactively
Optimize Router Placement Permanently
Position your router centrally in your home, elevated 3-4 feet off the ground on a shelf—not inside cabinets, behind TVs, or near metal objects. This maximizes signal reach to outdoor Ring devices. For multi-story homes, consider placing the router on an upper floor since signals travel downward more effectively than upward.
Implement Monthly Maintenance Routine
Check your doorbell’s Device Health status monthly to catch signal issues early. Clean the device housing periodically to prevent dirt buildup that could interfere with components. Before holiday seasons, verify no new furniture or decorations obstruct the router-to-doorbell path. These simple habits prevent 80% of recurring Wi-Fi connection problems with Ring devices.
Your Ring doorbell’s Wi-Fi connection is the lifeline to all security features—without it, you lose notifications, live view, and recording capabilities. By systematically checking these elements—from quick app diagnostics to network infrastructure—you’ll quickly identify and resolve connectivity issues. Start with the simplest checks like battery level and app status, then progress through deeper solutions as needed. Most Wi-Fi problems resolve within 10 minutes using these proven steps, keeping your home security system running reliably year-round.